Abstract
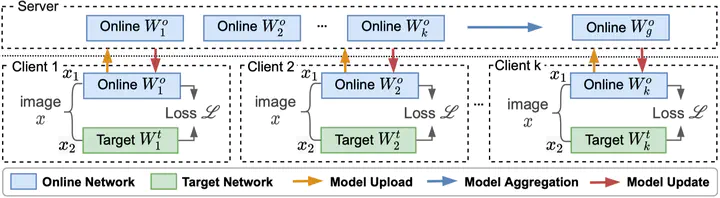
Self-supervised learning (SSL) is capable of learning remarkable representations from centrally available data. Recent works further implement federated learning with SSL to learn from rapidly growing decentralized unlabeled images (e.g., from cameras and phones), often resulted from privacy constraints. Extensive attention has been paid to SSL approaches based on Siamese networks. However, such an effort has not yet revealed deep insights into various fundamental building blocks for the federated self-supervised learning (FedSSL) architecture. We aim to fill in this gap via in-depth empirical study and propose a new method to tackle the non-independently and identically distributed (non-IID) data problem of decentralized data. Firstly, we introduce a generalized FedSSL framework that embraces existing SSL methods based on Siamese networks and presents flexibility catering to future methods. In this framework, a server coordinates multiple clients to conduct SSL training and periodically updates local models of clients with the aggregated global model. Using the framework, our study uncovers unique insights of FedSSL: 1) stop-gradient operation, previously reported to be essential, is not always necessary in FedSSL; 2) retaining local knowledge of clients in FedSSL is particularly beneficial for non-IID data. Inspired by the insights, we then propose a new approach for model update, Federated Divergence-aware Exponential Moving Average update (FedEMA). FedEMA updates local models of clients adaptively using EMA of the global model, where the decay rate is dynamically measured by model divergence. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FedEMA outperforms existing methods by 3-4% on linear evaluation. We hope that this work will provide useful insights for future research.